Metamorphic rocks
Metamorphism is the solid state transformation of preexisting rock into
texturally or mineralogically distinct new rock, as a result of high
temperature and pressure,
The new
rock ===== metamorphic rock in nearly all cases has a different texture
and very common different mineral composition from the original (called)
parent rock.
example.
Quartz
sandstone(SiO2)+calcite cement(CaCO3)===
wollastonite(CaSiO3)
+CO2
These changes occur in order to restore equilibrium for the gradually changign Pressure and temperature.
Principal
agents of metamorphism are:
1.Temperature
2.Pressure
3.Chemistry of the original (parent) rocks
1. Temperature
Changes
Mineral is
said to be STABLE, if given enough time it does not react to become a
new mineral.
Temperature is probably the most important factor in metamorphism. As
the temperature of the rocks changes the minerals become unstable and
react with other minerals to form a new mineral assemblage, that are
stable under the new conditions.
Heat is
also important because it increases the reaction rate.
(oven----
higher temp. burn everything)
Below
200°C the reaction rate is low, this is the sedimentary environment, and
rocks are stable for millions of years.
At extreme
temperature increase, minerals start to melt, and become igneous rocks.
At the transitional boundary, some rock forms. The rocks forming here
are called migmatite.
If a high
temperature metamorphic rock cools down, the minerals became unstable
again, however at the low temperature environment reaction rate is low,
these minerals are called METASTABLE
2. Pressure
changes
There are
two kinds of pressure:
Confining
Applied
equally on all surfaces (Hydrostatic)
Diver in
the water (his whole body has the same pressure everywhere)
This high
pressure tend to reduce the space occupied by the different minerals,
and can drive reactions which produce new minerals with closer atomic
packing.
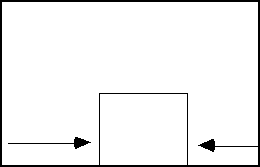
Directed pressure
Pressure
applied unequally on the surface of a body is directed or (DYNAMIC)
pressure. This pressure tend to deform objects into spindle-shaped or
flattened form.directed compressive pressure
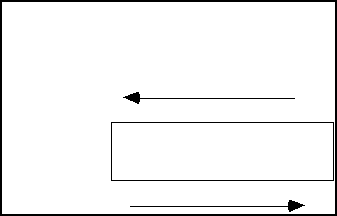
Caused by
directed pressure also, but here the parts of the body move or slide
relative to one another and parallel to the forces. (rolling pin)
The
pressure usually changes abruptly along tectonically active zones. (huge
pressure)
Under
pressure the minerals became ductile and can be slowly deformed as the
grains are slowly move and rotate. Deformation reorients the mineral
grains and form new texture.
3. Chemical
activity during metamorphism
Chemically
active fluids mostly water containing ions in solution, are also very
important in metamorphic processes. Some fluid occur in almost every
kind of rocks. In addition minerals stable at low P,T, such as
amphibole, clay, mica are contain OH in their crystalline structure. At
high T,P, this water is forced out from the mineral structure and is
good agent in the rock for further chemical changes. (The mineral
changes caused by the hot fluids are called METASOMATISM).
Texture of metamorphic rocks
Directed
pressure has important role in forming met. texture.
The
paralell aligment of textural and structural features of rocks are
called FOLIATION
Foliated textures
1.Slaty
The rock
splits along nearly flat and parallel planes indicating that
microscopic platy minerals were pushed into alignment during
metamorphism.

2.Schistose
Visible
needle-shaped minerals have grown essentially parallel to one another
during directed pressure
 facweb.bhc.edu/.../
labs/metamorf/Texture.htm
facweb.bhc.edu/.../
labs/metamorf/Texture.htm
3.Gneissic
Rock became very plastic
and the new minerals are separated into bundles of different minerals.
 facweb.bhc.edu/.../
labs/metamorf/Texture.htm
facweb.bhc.edu/.../
labs/metamorf/Texture.htm
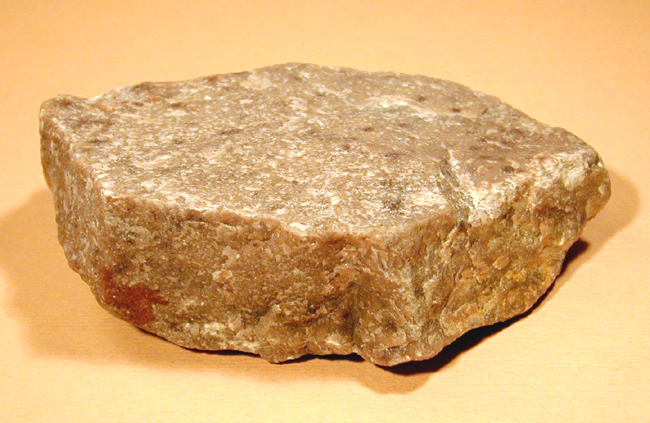
Nonfoliated texture
No directions, crystalline

from:www.gc.maricopa.edu/.../ imagearchive/marble.htm
PORPHYROBLASTS
Extremely
large crystals in metamorphic rocks
CLASSIFICATION OF METAMORPHIC ROCKS
CONTACT (THERMAL) METAMORPHISM
Igneous intrusion into "country rocks". Temperature is dominant.
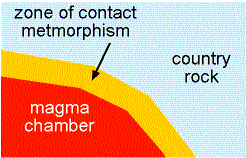
from:http://enterprise.cc.uakron.edu/geology/natscigeo/Lectures/smrocks/metafig.gif
DIRECTED
PRESSURE IS NOT IMPORTANT, THEREFORE THESE ROCKS ARE FREQUENTLY
NONFOLIATED.
COOKING
country rocks Contact metamorphism
AUREOLE (1
- 10 M WIDE)
SHALE IS
changed into hornfels, with visible micas
DYNAMIC
Along
fault zones, Pressure dominant temperature is not important
Fault
breccia, (force crashes the rock into small fragments)
Ductile
flow can form milonite along fault zone at larger depth
REGIONAL, OR DYNAMOTHERMAL
Both
temp. and Pressure
Low
medium
high
Some
minerals are good indicators for certain pressure and temperature range.
They are called Index minerals
Classification of Metamorphic rocks
Low Grade
slate
phyllite
chlorite
talc
Medium grade
Mica
schist
amphibolite
High grade
gneiss
ecklogite
|
Parent rock |
Low grade |
Medium grade |
High grade |
|
Shale, felsic igneous rock |
Slate, phyllite |
Mica schist |
gneiss |
|
Mafic igneous rocks |
Chlorite, talc schist |
amphibolite |
eclogite |
|
|
MARBLE |
||
|
|
Quartzite |
||