EARTHQUAKES
An
earthquake is a trembling or shaking of the ground caused by the sudden release
of energy stored in the rocks beneath the earth’s surface.
Elastic
rebound theory (Reid)
1.rock
with stress acting on it
2.Stress
hava caused strain in the rock. Strain builds up for a long period of time,
until the strain gets beyond the rock’s braking point.
3.
Rocks brake suddenly, releasing energy with rock movement along a fault. They
can move horizontally or vertically. Energy release happens in the form of
seismic waves.
Seismic
waves

After:http://www.geog.ouc.bc.ca/physgeog/contents/10m.html
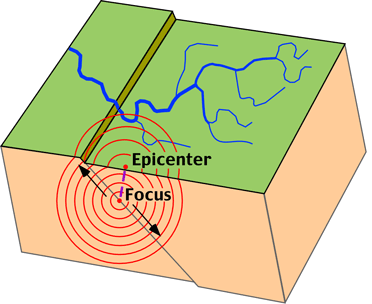
The
point within the earth where seismic waves originate is called the focus of the earthquakes. This is the center of the earthquake, the
point of the initial movement along the fault.
EPICENTER:
Is the
point on the earth’s surface directly
above the focus.
There
are two types of seismic waves:
BODY
WAVES:
These
waves are traveling through the earth’s interior spreading from the focus in
every direction (like sound waves in air).
There
are two kind:
P
WAVE (primary)
is
a compressional (longitudinal) in which the wave travel parallel to the
direction of wave propagation. This is a very fast wave traveling with 4-7
km/sec speed. Because it is fast usually this is the first (primary) wave to
arrive to a recording station after an earthquake.

After:
http://www.educ.uvic.ca/Faculty/jtinney/earth%20science/Earthq.html#Earthquake
S
WAVE (secondary)
It
is slower, Transfer wave that travels 2-5 km/ sec. An S wave is propagates by a
shearing motion, much like a shaken rope. The
rock vibrates perpendicular to the wave direction.

After:
http://www.educ.uvic.ca/Faculty/jtinney/earth%20science/Earthq.html#Earthquake
They
both pass easily through solid rocks. S wave can not pass through fluid. They
are usually faster in dense rock and slower in unconsolidated sediments.
SURFACE
WAVES
They
travel on the surface away from the epicenter (like water waves if we throw a
pebble into the water. They are
slow waves, but they cause all the damage, because they cause ground movement,
and since they are slow it takes longer to pass through.
LOCATION
AND MEASURING EARTHQUAKES
Seismograph
Is the equipment which are able to record of the earth motion usually in the form of wiggle line drawn on a strip of paper.

After:http://www.geo.mtu.edu/UPSeis/locating.html
The paper record is called SEISMOGRAM.

After:http://www.geo.mtu.edu/UPSeis/locating.html
There
is a network of seismographs throughout the earth to record and study
earthquakes.(also nuclear bomb explosions)
Within
minutes after an earthquake happen somewhere distant seismographs begin to pick
up seismic waves. A large one would be detected everywhere on the earth.
Because
of the difference in the speed of the different waves, people can locate
earthquakes, and also study their strength and effects.

After:http://www.geo.mtu.edu/UPSeis/locating.html
Determination
of the earthquake location
Seismogram
tells how fare the earthquake happened, but does not give direction.

Depth
of the earthquakes
The
max. depth is 670 km. They are classified into three groups.
1.
Shallow
0-70 km 85%
2.
intermediate focus
70-350 km
12%
3. Deep
focus
350-700 km
3%
The
shallow focus quakes are more common, because rocks are more brittle on the
surface.
EARTHQUAKE
STRENGTH
The
strength or size of the earthquake is measured in two ways
1. INTENSITY
This is
a measure of the damage caused by the earthquake on humans and buildings.
Intensities are pressed in roman numerals I-XII on the modified MERCALLI SCALE, where higher numbers indicate more damage.
 Giuseppe
Mercalli (From Walker, 1982)
Giuseppe
Mercalli (From Walker, 1982)
VI.
everybody feels it, the are scared run 0utdoors (damaged chimneys)
VII.
Damage slight. Partial collapse in weak bedly designed buildings
VIII.
Damage slight in well designed building, worse in poorly designed ones. so on.
XII.
damage is total.
There
is a problem of using this scale, bec. it is only measures destroy, and there is
big difference in building designes. Underlying geology is also important.
Houses built on solid rocks are much better for surviveing than unconsolidated
sediment.
2. The
second method is to measure the Magnitude
of the earthquake (RICHTER SCALE).
In this method is people calculate the energy released during the quake.
People are measuring the amplitude of one of the wiggles on the seismogram.
(common in US). After measuring the wiggle amplitude and correcting for the
distance and the specific seismograph, scientist can assigne a number called
MAGNITUDE.
 Charles
Richter studying a seismogram (From Walker, 1982)
Charles
Richter studying a seismogram (From Walker, 1982)
|
Richter Scale |
Energy Released |
Comment |
|
2.0 |
6.3 x 10 7 |
Smallest earthquake detectable by people. |
|
5.0 |
2.0 x 10 12 |
Energy released by the Hiroshima atomic bomb. |
|
6.0 - 6.9 |
6.3 x 1013 |
About 120 shallow earthquakes of this magnitude occur each year. |
|
6.7 |
7.1 x 1014 |
Northridge, California earthquake 1994. |
|
7.0 |
2.0 x 1015 |
Major earthquake. |
|
7.4 |
7.9 x 1015 |
Turkey earthquake August 17, 1999. More than 12,000 people killed. |
|
7.6 |
1.6 x 1016 |
Deadliest earthquake this century. Tangshan, China, 1976. About 250,000 people died. |
|
8.3 |
1.8 x 1017 |
San Francisco earthquake of 1906. |
|
8.6 |
5.0 x 1017 |
Most powerful earthquake recorded in the last 100 years. Southern Chile 1960. Claimed 5,700 lives. |
The
richter scale goes from 1 -8.6, and there is no upper limit. It is a logarithmic
scale the difference between 1 and 2 is ten times. Earthquake with larger
amplitude than 9 is unlikely to occur because it seems that this is the upper
limit of elastic strength beyond which rocks will brake.


| Distribution of earthquakes with a magnitude less than
5 on the Richter Scale on the left,and with a magnitude greater than 7
on the right.
After: http://www.geog.ouc.bc.ca/physgeog/contents/10m.html. |
Erathquakes
in USA

Only a
few loc. are earthquake free.
Most of
the large ones occur in the western part of the US.
EFFECT
OF EARTHQUAKES
GROUND
MOTION
This is
the trembling and shaking of the land that can cause the buildings to vibrate.
In large quakes the motion is visible.
Because
proper building construction can reduce the damage in a grat deal, building
codes has to be very strict in special areas. Their location also has to be
controlled. (hard rock!!!)
FIRE
Prticularly
serious problem after an earthquake, because broken gas and water pipes, and
fallen electrical wires.
(San
Francisco 1906)
LANDSLIDES
They
can be triggered by shaking the ground (1959 Madison Canyon) 1970 Peru huge mud
flows in the Andes!!
PERMANENT
DISPLACEMENT OF THE SURFACE
AFTERSHOCKS
small earthquales following the big ones. Although they are smaller they still can cause damage in the weakened constructions.

A
view of a parking lot on the campus of California State University. Columns of
reinforced concrete failed after the 1994 Northridge earthquake and its
aftershocks. (Source: Photography by M. Celebi, US Geological Survey.
Image provided by the National
Geophysical Data Center, NOAA).
TSUNAMIS
Seaquake;
initiate huge wave.... (seismic sea waves) Hurricane can have 400 m, however a
tsunamis may have a wavelength of 100
miles and may be moving 450
miles/hour. The wavw height near the shore is 15-30 m.
Because
of the long wavelength of the tsunamis it will not withdraw fast, but the water
will rise for 5-10 minutes, causing flood.

| The earthquake of March 27, 1964, in the Gulf of Alaska generated a tsunami. This photo shows a beached fishing boat that was carried landward by the tsunami wave. (Source: Image provided by the National Geophysical Data Center, NOAA). |
LIQUEFACTION
In
areas where unconsolidated sediment ids water filled, during the quake the
sediment turns into liquid that is not capable to support buildings. Buildings
will collapse an sewege tanks and other underground constructions will float up
to the surface.

Earthquake of June 16, 1964 in Niigata,
Japan had a magnitude of 7.4. Liquefaction
of some soils in the area caused large apartment buildings to tip over on their
sides. (Source: Image provided by the National
Geophysical Data Center, NOAA).
DISTRIBUTION
OF EARTHQUAKES
shallow
deep PLATE BOUNDARIES!!!!
EARTHQUAKE
PREDICTION
-MONITORING
OF SLIGHT CHANGES ALONG FAULT ZONES.
-BEFORE
LARGE QUAKES, SMALL CRACKS CAN FORM ALONG THESE ZONES; THE PROPERTIES THE ROCKS
CAN BE CHANGED, BECAUSE OF THE SMALL CRACKS.
-WATER
LEVELS IN WELLS MAY RISE
-SURFACE
OF THE EARTH TILTS AND SLIGHTLY CHANGES ELEVATION
-CHINESE
SCIENTISTS CLAIM PREDICTION BASED ON ANIMAL BEHAVIORS: HORSES BECAME SKITTISH,
SNAKES LIVE THEIR HOLES
(IN
1975 CHINESE PREDICTED AN EARTHQUAKE 5 HOURS BEFORE)